Many adults treat stomach problems as frivolously as migraines - “it will hurt and pass away.” But if a daughter or son complains of such a malaise, it is simply necessary to pay attention, and do not even think of attributing such behavior to whims and the desire to draw attention to yourself. How to cope with this problem, with abdominal pain what to give the child from the medicine? A detailed description of the symptoms of common diseases and the answer to the question of when you can not postpone a visit to the doctor - especially for you in our article.
Will it hurt and pass?
Pain in the abdomen in children can occur for a variety of reasons. So, if the child did not fall and hit, but complains of malaise, you should quickly analyze his nutrition in the last days. Sharp abdominal pains can occur with banal overeating, eating incompatible products together, harmful or poor-quality / spoiled food.
In this case, a digestive system disorder can be manifested not only by unpleasant sensations, but also be accompanied by symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, bloating and flatulence. If the baby ate something new for itself or frankly harmful before the deterioration of well-being, you can not panic. Also, do not worry if you have doubts about the freshness / quality of the products or if the child simply overeats - which often happens during the holidays.
The treatment in this case is simple - do not feed the baby for a while, but do not limit it to drink and wait until the sharp abdominal pains disappear. You can give plain water or sweet black tea. It is especially important to prevent dehydration with loose stools. Offer your child drinks, even if he doesn’t ask, and remind you to drink.
With diarrhea, activated charcoal or Smecta can be given in a dosage appropriate for age. However, if the child's condition worsens or remains unchanged after 6 hours after the onset of the first symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
When is a specialist consultation necessary?
Three types of pain are distinguished: aching, acute and colic (usually observed in newborn babies). Ask your child to describe your malaise as accurately as possible. The most dangerous is acute or dagger pain. This is a strong and ongoing discomfort that can also give off to neighboring areas and parts of the body. Will the usual remedies for abdominal pain be suitable in this case, what should I give the child to alleviate his condition? Each parent must remember that stomach discomfort can cause serious illness.
If the pain is acute, you should immediately consult a doctor or even call an ambulance. Prior to the arrival of a specialist, do not give medicine, try to distract the child and improve his condition - gently stroke his stomach, talk with the baby or show him a cartoon.
So, the indications for urgent hospitalization or calling a doctor is a prolonged intense pain. In this case, the child cannot find a place for himself, rushing around and screaming. If any pain lasts more than three hours, and there are no improvements, it is better not to delay the appeal for qualified help. Blood in the stool or vomiting is a definite reason to call an ambulance.
A quick reaction is required from the parents if the child has eaten / drank some medicine, a household chemical product or other dangerous and harmful substance. Before the arrival of the doctor, it is not recommended to give drugs that eliminate the symptoms, and to use traditional medicine. Lay the child down and help him take the most comfortable position.
Tummy problems in the smallest
 Young parents find it difficult to care for a newborn, not only because of a lack of experience. The baby cannot explain his feelings and complain to the parents. How to understand that a baby has a stomachache? Kids express their dissatisfaction with the only available means - crying. If the child does not sleep well, eats little or does not eat at all - most likely, the reason is colic.
Young parents find it difficult to care for a newborn, not only because of a lack of experience. The baby cannot explain his feelings and complain to the parents. How to understand that a baby has a stomachache? Kids express their dissatisfaction with the only available means - crying. If the child does not sleep well, eats little or does not eat at all - most likely, the reason is colic.
Also, with problems with the tummy, the baby bangs its legs and pulls the knees to the chest. Many babies have colic and usually stop at the age of 4-6 months; they do not require special treatment. If the child’s anxiety is accompanied by fever, vomiting, the appearance of blood in the feces, an urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary. The symptoms described above may indicate food allergies or bowel obstruction.
Preschooler's stomach hurts

To assess the condition and well-being of a child under the age of 2 years is possible only by his behavior and mood. If the child is inactive, cries and refuses to eat - it is likely that the problem is in the stomach. Moreover, at the age of over one year, the causes of digestive problems are most often “adults”: food poisoning and allergies, overeating, infectious diseases.
At the age of more than 2 years, many children can consciously explain what exactly hurts them or show them with their hands. After listening to the complaints of the child, parents should compare and analyze all the symptoms. If the abdominal pain in a child of 5 years is irregular and has appeared recently, and the general condition of the baby is good, you can try to cope with the problem at home. Invite your child to sleep or just lie quietly. Give the right medicine for better digestion.
Similarly, you can do with diarrhea or vomiting (if symptoms are observed separately). Remember that loose stools (over a short period of time) are just a sign of a simple digestive upset, and one-time vomiting can occur due to coughing or overeating.
My stomach hurts, but not my stomach ...
Systematic discomfort in any part of the body is an occasion to go to the hospital. An interesting fact is that abdominal pain and nausea in a child can occur without any physiological reasons. In this case, most likely, the whole matter is in the patient's psycho-emotional state. This phenomenon is called functional pain. Moreover, examinations of internal organs do not show any deviations from the norm. The reason most often lies in overwork, overload of the nervous system, unrest and stress. This may seem strange, but you should consult a psychologist to treat such pain. However, in any case, starting with a visit to a gastroenterologist and examination is worth starting. Remember that regular abdominal pain in the navel in a child can also indicate pathologies of the internal organs.
How to treat functional pain?

If the child regularly complains of discomfort, the most important thing for parents is to keep calm. You can’t ignore these complaints and frankly “not hear” the child, but it’s also not worth it to make a fuss every time a little stomach hurts. Visit a specialist is necessary. And once it is confirmed that the pains are truly functional, treatment can begin.
Start keeping a special "diary of the abdomen." It should be written down all bouts of pain, indicating in which situations they appear, and that helps to feel better. An analysis of these notes by a doctor will help establish the specific causes of the problem and help reduce the intensity of discomfort, and then completely forget about them. Parents should try to create a favorable atmosphere at home and somehow captivate the baby. You can offer him to start visiting sections and hobby groups, or come up with some kind of home-grown hobby for the child.
What medications can be given to relieve stitching pains in the abdomen? If you are sure that the discomfort appears against the background of psychological problems, you can give "Ibuprofen" or another universal pain medication suitable for the child's age. After a quiet rest and sleep, the functional pain also recedes - offer the child a good rest.
 Self-medication is undesirable, and sometimes completely unsafe. But we all know that situations are different. How to choose a suitable drug for abdominal pain, what to give the child to eliminate unpleasant symptoms? In order to normalize digestion when overeating or eating poorly combined foods, you can try to take drugs such as: Mezim, Festal, Creon. With diarrhea and nausea, you can take "Gastrolit" or "Regidron." Heartburn in children is treated with "Maalox", "Rennie", "Almagel".
Self-medication is undesirable, and sometimes completely unsafe. But we all know that situations are different. How to choose a suitable drug for abdominal pain, what to give the child to eliminate unpleasant symptoms? In order to normalize digestion when overeating or eating poorly combined foods, you can try to take drugs such as: Mezim, Festal, Creon. With diarrhea and nausea, you can take "Gastrolit" or "Regidron." Heartburn in children is treated with "Maalox", "Rennie", "Almagel".
What medicine from an adult first-aid kit will help with stomach pain, what should I give my child if there are no special medicines for children at hand? A universal remedy for discomfort in the abdominal cavity is considered to be "No-spa". This drug relieves attacks of urolithiasis and allows you to feel better with spastic constipation. If all the symptoms of food poisoning (vomiting, diarrhea and stomach pain) are observed at the same time, you can try to give your child activated charcoal, Enterodes or Smecta. Caution: before giving the child any medicine, carefully read the annotation and accurately calculate the dosage according to the age or weight of the baby. If possible, even with home treatment, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Attention infection!
Infectious diseases are what many parents are most afraid of. Do not panic, as with any other illness, the most important thing is to make a diagnosis on time and correctly. Pain in the left abdomen, in the right or near the navel - all these symptoms can be a manifestation of an infection. It is important to understand that diseases of this category can affect various organs and differ in the type of pathogen by: viral, bacterial and mixed.
With infections of the genitourinary system, a change in urination is observed. In this case, the child complains of abdominal pain and often goes to the toilet. Elevated body temperature, diarrhea and vomiting are signs of most infectious diseases. Remember that any infection is quite dangerous. Accordingly, at the first suspicion that the disease is caused by viruses or bacteria, you must contact the clinic.
Symptoms of Appendicitis
 Appendicitis is often considered a disease of a purely adult, and this is a big mistake. In fact, this pathology is often observed in children older than 1.5 years. In infants, appendicitis is indeed very rare. But schoolchildren of 10-12 years old are often given this diagnosis, it is believed that boys are most susceptible to it.
Appendicitis is often considered a disease of a purely adult, and this is a big mistake. In fact, this pathology is often observed in children older than 1.5 years. In infants, appendicitis is indeed very rare. But schoolchildren of 10-12 years old are often given this diagnosis, it is believed that boys are most susceptible to it.
Appendicitis is especially dangerous at a young age. The sooner the correct diagnosis is made and treatment is started, the more effective it will be and the risk of developing dangerous complications will be less. By what signs can this pathology be recognized?
If the child complains of abdominal pain constantly, and he does not feel better after sleep, a visit to the doctor is required! Moreover, the localization of unpleasant sensations can be different. The classic version of pain is not always observed - on the right, below the stomach. Discomfort can also be felt near the navel or in the epigastrium. Parents should also be warned by the fact that abdominal pain in the navel in a child occurs when the body position is changed, coughing or crying. Vomiting or diarrhea may sometimes occur. With appendicitis, body temperature usually rises, the child himself becomes lethargic and drowsy, may refuse to eat. It is impossible to give painkillers or other medications for such symptoms - you should immediately consult a doctor.
Other common causes of abdominal pain
There is no child who does not accidentally fall or participate in a fight. Even the calmest and most peaceful baby can be pushed by peers or from time to time he stumbles on his own. What should I do if, after getting injured, complaints of abdominal pain begin?
Damage to the abdominal cavity is open and closed. In the first case, it is necessary to call an ambulance, which hospitalizes the patient. In the second - you should try to assess the general condition of the child. If there are complaints of pain, but the baby is still active, does not refuse food and sleeps normally - most likely, nothing serious has happened, but in this case, specialist advice will not be superfluous.
If vomiting occurs, increased heart rate, and general weakness after receiving an injury, you should go to the hospital immediately. Pay special attention if the child complains of pain in the left abdomen. In this case, damage to the spleen is possible.
A lot of anxiety is delivered to children and hernias. They can be internal and superficial, sometimes felt on the stomach. Unpleasant sensations arise when the hernia is pinched, self-medication in this case is impossible - you need to visit a doctor and prescribe a suitable treatment option.
Do not forget about diseases such as ulcers and gastritis. It was once believed that only adults are affected. But today, increasingly, these diagnoses are made to adolescents and even younger students. What is curious - the reason is not always lies in malnutrition, at risk are children taking certain drugs with courses and suffering from some chronic diseases.
Special attention should be paid to the child’s complaints of stitching pains in the abdomen if the baby underwent surgical treatment not too long ago. And this is another case when a doctor should be consulted immediately for diagnosis and treatment.
Source: FB.ru
Respiratory infections of viral origin can be accompanied not only by damage to the respiratory tract, but also by symptoms from other body systems. In particular, there are often abdominal pains, especially in children. A similar sign inspires parents with a lot of fears, so you need to figure out why it arises.
Pain in the abdomen can be associated with various pathological processes. If we are talking about a respiratory infection, then several options for the development of events are possible against its background. First of all, you should think about the effects of intoxication. In children, it is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and even abdominal pain. Some viruses (flu, for example) have tropism not only to the epithelium of the respiratory tract, but also to the nervous system. And in some cases, this can even manifest itself as an abdominal syndrome.
In clinical practice, diseases are often found, accompanied by changes in both the respiratory and digestive tract. These include the following infections:
- Adenovirus.
- Mononucleosis.
- Enterovirus.
It is not necessary to completely exclude the fact that pain can be a sign of not SARS, but a concomitant pathology. There are many conditions that can give a similar picture: therapeutic (chronic gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, colitis, peptic ulcer), surgical (appendicitis, intestinal obstruction), infectious (salmonellosis, dysentery), etc. It is likely that some kind of pathological process may be present in the patient at the same time as the common cold. But each of the cases requires individual consideration.
Can a stomach ache with ARVI and what causes it, the doctor will say after an appropriate examination.
Symptoms
Any acute abdominal pain is a signal for immediate medical attention, because they can indicate a dangerous condition, behind which complications are hidden. But even tangible discomfort in a child should alert parents. It’s impossible to figure out what is happening on your own, so the only way out is to consult a specialist. To make a diagnosis, the doctor will conduct a clinical examination, which includes an analysis of complaints, medical history and the search for objective signs of pathology.
Adenovirus infection
There are various clinical forms of adenovirus infection. Common to them will be damage to the respiratory tract, fever and intoxication syndrome. The main symptoms of the disease include:
- Nasal congestion, discharge (rhinitis).
- Persistence and sore throat (pharyngitis).
- An increase in tonsils, the appearance of plaque (tonsillitis).
- Eyelids, redness, swelling of the eyelids (conjunctivitis).
Specific for adenovirus infection will also be an increase in lymph nodes: both regional and distant - axillary, inguinal, intraperitoneal. Accumulation and reproduction in the latter pathogen just becomes the cause of mesadenitis and abdominal pain. In addition, the liver with the spleen may increase, which creates additional discomfort and discomfort.
A special form of adenovirus infection is gastroenteritis. It occurs with diffuse abdominal pain and diarrhea. And in children, the disease can be complicated by intestinal invagination. But against this background, respiratory symptoms are almost always present.
Infectious mononucleosis

If the stomach hurts with ARVI in a child, then you have to think about infectious mononucleosis. This is a pathology that proceeds with a noticeable polymorphism of the clinical picture. The infection begins with prodromal phenomena: headaches, malaise, loss of appetite. In the future, the temperature rises, sore throat appears and various groups of lymph nodes increase. These signs are included in the classical triad with mononucleosis.
Sore throat appears due to the phenomena of pharyngitis and tonsillitis. The back wall of the pharynx is reddened, granular, tonsils enlarged, often covered with plaque. First, the cervical lymph nodes increase, and then others, including the peribronchial and intraperitoneal (mesenteric) ones. This causes additional symptoms in the form of cough and abdominal pain. The latter can be quite pronounced, especially in children.
As with adenovirus infection, there is an increase in the liver and spleen (hepatosplenomegaly). This causes severity and discomfort in the hypochondria, sometimes sclera is yellowish. In some patients, small rashes appear on the skin. In adulthood and in children under 2 years of age, the disease is often asymptomatic.
Respiratory symptoms similar to ARI are common in patients with mononucleosis. In this case, abdominal pain occurs due to enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes.
Enterovirus infection

Pain in the abdomen during acute respiratory viral infections in children can also occur in cases where the infection is caused by enteroviruses. The onset of the pathology is acute - with fever, malaise, and body aches. Against the background of damage to the respiratory system (sore throat, runny nose, redness of the posterior pharyngeal wall), signs of gastroenteritis appear:
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea.
- Stomach ache.
The stool becomes more frequent up to 7-10 times a day, which can cause dehydration, especially in young children. In infancy, enterovirus infection proceeds harder and longer, often gives complications (pneumonia, meningitis, myocarditis).
Additional diagnostics

To establish the source of symptoms, you need to conduct an additional examination. Clinical symptoms only suggest a disease, but the final diagnosis is based on the results of laboratory and instrumental examination:
- General blood and urine tests.
- Blood biochemical parameters (inflammatory markers, proteinogram, electrolytes).
- Serological tests (the appearance of specific antibodies).
- Throat and nose swabs.
- Feces analysis.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
In concomitant diseases, a more thorough examination of the digestive tract, including fibrogastroscopy, may be required. Abdominal pain may require consultation with an infectious disease specialist, gastroenterologist, and surgeon. And only after a comprehensive diagnosis will it be possible to establish the cause of the discomfort, which will become the basis for further therapy.
If the stomach hurts with SARS in a child , you need to go to the pediatrician to determine the cause. First of all, he will direct the patient to undergo some laboratory tests, after which he will establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment. It is strongly not recommended to give medications on your own, which can provoke a deterioration in the well-being of the child, leading to serious consequences.
There can be several causes of abdominal pain. To establish an accurate diagnosis, you must visit a doctor. An abdomen with acute respiratory infection can become ill due to:
- Conducting drug therapy, since many drugs have a side effect in the form of the development of pain in the abdominal cavity.
- Increase in temperature indicators. This condition, as a rule, is accompanied by an increase in the level of acetone, the manifestation of which is epigastric pain.
- The negative effects of the pathogen. Pathogens enter the gastrointestinal tract, due to which there is a disruption in the functioning of some organs and systems.
- Purulent discharge, mucus from the nasal cavity into the body with a runny nose. After this, an indigestion may occur, pain may occur.
Epigastric pain may occur with the development of the following infections:
- adenoviral;
- mononucleosis;
- enterovirus;
- rotavirus.

Also, one cannot exclude the appearance of such painful sensations with:
- cholecystitis;
- gastritis;
- pancreatitis;
- stab;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and / or duodenal ulcer;
- appendicitis;
- bowel obstruction;
- salmonellosis;
- dysentery.
Do not delay the visit to the doctor, as some of the diseases presented require immediate surgical intervention.
Symptoms
Any pain that occurs in the abdomen in a child is an occasion to visit a pediatrician. In acute abdominal pain, an ambulance must be called to avoid serious consequences. Next, we consider the symptoms characteristic of the development of each of the presented diseases.
Adenovirus infection
The course of adenovirus infection is accompanied by damage to the respiratory tract, fever, intoxication of the body. Among the main clinical signs can be distinguished:
- Cough, sore throat.
- Discharge from the nasal passages, nasal congestion.
- Swelling of the eyelids, the appearance of burning, redness of the visual organ.
- Swollen tonsils, the appearance of plaque on them.
This disease can also cause mesadenitis (swollen abdominal lymph nodes). In this case, the active reproduction of pathogenic bacteria occurs, which causes the development of pain in the abdomen. In addition, inflammation can go to the liver, spleen, which also brings unpleasant sensations.

Adenovirus infection can cause gastroenteritis, in which diarrhea and epigastric pain appear. Children are most susceptible to the development of complications - intestinal intussusception, accompanied by respiratory symptoms.
Infectious mononucleosis
When the symptom in question appears, the development of infectious mononucleosis can be assumed. At an early stage of the disease occurs:
- headache;
- malaise;
- deterioration / loss of appetite.
After some time, the main symptoms characteristic of this pathology appear:
- increase in body temperature;
- a sore throat;
- an increase in the size of the lymph nodes.
Pain in the throat occurs due to the development of tonsillitis and pharyngitis. At the same time, tonsils swell, often a plaque appears on them, the back of the throat turns red, lymph nodes become inflamed (first the neck). This provokes the occurrence of other unpleasant symptoms - intense abdominal pain and cough. The liver, spleen may also increase, sclera yellowness, a small skin rash appear.
It is worth considering that in children under the age of two, in adults, infectious mononucleosis is most often asymptomatic.
Enterovirus infection
This type of pain can occur due to infection with an enterovirus infection that has an acute onset. When this appears:
- malaise;
- fever;
- muscle aches, joints.
Against the background of respiratory disorders (cough, runny nose, redness of the posterior pharyngeal wall), a clinical picture arises that is inherent in gastroenteritis (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain). The stool becomes more frequent (up to 10 r./day), as a result of which dehydration may develop. This pathological condition is extremely dangerous, especially for infants. Disease of enterovirus infection at an early age is more severe, can lead to serious complications:
- myocarditis;
- pneumonia;
- meningitis.
Therefore, it is very important to consult a pediatrician in a timely manner to determine the diagnosis and prescribe the necessary therapy.
Rotavirus infection
Rotavirus infection is characterized by the appearance of:
- Vomiting, nausea.
- Increase in temperature indicators.
- Ailments, general weakening of the body.
- Rapid stool of fluid consistency.
- Intense, sharp abdominal pain.
- Sore throat.
- Redness of the optic organ and mucous membrane of the pharynx.
With the development of such symptoms, it is necessary to seek medical help, since frequent defecation can lead to dehydration due to rapid loss of fluid.
Additional diagnostics
Based on clinical signs, we can only make an assumption of the occurrence of a disease. To establish an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo several laboratory tests:
- KLA (general blood test).
- OAM (general urinalysis).
- Blood chemistry.
- Serological tests.
- Fecal analysis.
- Taking a smear from the nose, pharynx.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity.
The doctor can also refer the patient to fibrogastroscopy for a more detailed examination of the gastrointestinal tract. Sometimes there is a need to visit an infectious disease specialist, surgeon, gastroenterologist.

What to do?
With the development of acute respiratory infection and all the associated symptoms, parents should provide the child with bed rest, include in the menu a plentiful drink. Do not give any medications on your own, which can significantly worsen the condition of the child, leading to serious consequences. To do this, you need to consult a specialist, for acute pain - call a doctor at home.
Drug treatment
Based on the results of the tests, the pediatrician should prescribe drug therapy aimed at destroying the flu virus, the common cold:

- Candles Viferon. The medicine is great for fighting viruses, it is indicated for use for an early age. Suppositories are used to eliminate pains, intense abdominal pain caused by rotavirus infection.
- Interferon It is prescribed for acute respiratory viral infections, it is approved for use from birth.
- Anaferon for children. The drug helps to stop the inflammatory processes that occur in the upper respiratory tract, increases the protective properties of the child's body.
- Drops Derinat. Buried in the nasal cavity with acute respiratory viral infections, colds.
- Grippferon. The drug has an antimicrobial effect.
If during SARS, the stomach hurts, the doctor may prescribe enzyme preparations:
- Penzistal. Improves the digestion process, eliminates any discomfort in the stomach.
- Mezim. Helps to stabilize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, eliminate digestion disorders.
- Festal. It is used to improve the assimilation, breakdown of food products, normalizes metabolic processes.
Also, the pediatrician can prescribe immunomodulating medications, drugs to eliminate respiratory symptoms, antipyretic drugs (so that the temperature drops), antiemetics, sorbents, antibiotics (for bacterial infections).
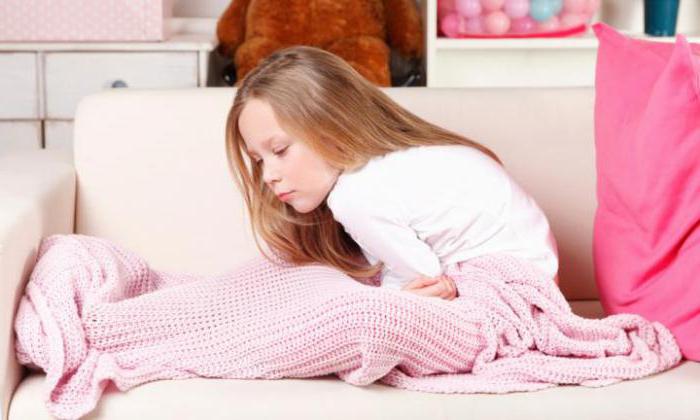
What to do if a child has a stomach ache, is it limited to simple painkillers, consult a doctor or urgently call an ambulance? Each parent has to deal with such issues. The causes of abdominal pain in a child can be either the most common or indicate a serious illness. At the same time, getting an accurate and detailed description from a child of what exactly hurts him is not so simple. Fortunately, in most cases, abdominal pain in children does not pose any danger and pass quickly.
Causes of abdominal pain in children
- Infections If viruses and bacteria enter the child’s body, they can cause abdominal pain and cause a disease called “gastric” or “” (gastroenteritis). As a rule, diseases caused by viral infections pass quickly, while bacterial diseases may require antibiotics.
- Food. Food poisoning (their symptoms are similar to those of gastroenteritis), food allergies, eating too much food, increased gas formation - all these cases can cause bloating and a child’s complaints of pain. In such cases, pain begins shortly after eating.
- Poisoning. This can range from ordinary ordinary troubles (for example, when a child ate soap) to more serious problems, such as swallowing pins, magnets, coins, botulism caused by expired products, or the result of an overdose of drugs (e.g. paracetamol).
- Diseases requiring surgery, such as or bowel obstruction.
- Complications of diseases not related to the digestive system. For example, a child may experience abdominal pain with diabetes.
Symptoms
Parents or other relatives usually quickly notice that something is wrong with the child. Very young children can cry when they are bent in half, and when lying down, they curl up in the embryo's pose and pull their knees to their chest. Older children usually immediately say that they have a stomach ache. And adolescents sometimes consider it a matter of honor to endure pain, and the parent has to balance between fears for the child’s health and how he would not heal even more.
If a child complains of abdominal pain, it is first necessary to clarify the following circumstances:
- How long the stomach hurts. In the simplest cases that do not require medical intervention, the pain will soon disappear (for example, with increased gas formation caused by the consumption of an inappropriate product, or with uncomplicated cases of gastroenteritis). Such pain usually does not last long. But if the child often has a stomach ache or a separate attack of pain lasts more than a few hours, you should consult a doctor.
- Duration of pain. If the cause of abdominal pain was gastrointestinal flu or gas, the pain goes away in a few hours. But if it lasts more than a day, you should consult a doctor.
- Where exactly does the stomach hurt? Do not worry too much if the child hurts in the middle of the abdomen (in these cases, when asked to demonstrate exactly where the pain hurts, the child indicates the navel area). The situation is more serious if the abdomen hurts in other places, especially if the pains are localized in the lower part of the right side of the abdomen - appendicitis is just there.
- Well-being of the child. If your child has a bad stomach ache and looks very bad, you should seek medical help. What does "very bad" mean? First of all, you need to pay attention to skin color (pallor), the presence of perspiration, drowsiness, lethargy. Cases are worrying if the child cannot be distracted from the pain by playing or he refuses to drink or eat for several hours.
- Vomiting Children often vomit with abdominal pain, but it alone cannot serve as an indicator of the severity of the disease. As with pain sensations, the main rule is that if vomiting lasts more than a day, you should consult a doctor.
- The nature of the vomiting. If vomiting is greenish or yellow in infants or children 2–3 years old, a doctor should be called. If vomiting contains blood that is clotted or fresh, you should seek emergency help.
- Diarrhea. Abdominal pain is often accompanied by diarrhea. As a rule, this circumstance indicates that the disease is caused by an infection. Diarrhea can last up to three days. If blood is visible in the feces, consult a doctor.
- Heat. High temperature alone is not critical in assessing the severity of a situation. Many dangerous diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are accompanied by normal temperature.
- Groin pain. Sometimes children say that their stomach hurts, although it actually hurts in another place, for example, when the testicle is twisted in male children. Inversion of the testis occurs when the testicle turns and thereby pinches the nerves in the spermatic cord. The child may be shy to name a specific place, so you need to ask if he has any “lower” pains. In the early stages, testicular torsion is easy to correct, but the longer it lasts, the harder it is to cure. So if a child complains of pain in the groin, you should immediately consult a doctor.
- Difficult urination. If a child experiences abdominal pain and problems with urination (for example, it is too frequent or painful), these circumstances may indicate the presence of an infection in the body. You should consult a doctor.
- Skin rashes. Some dangerous diseases are also accompanied by a rash. In such cases, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Establishing diagnosis
A child’s abdomen can hurt for a number of reasons that affect several organ systems, each of which requires its own diagnostic tests. The doctor will examine the child’s medical history, conduct an examination, which may include examining the rectum for blood. And already on the basis of the information received, the doctor may suggest the following tests.
Another doctor may offer to do an x-ray of the abdominal cavity, ultrasound of the abdomen or testicles and computed tomography of the abdomen. Also, depending on the condition of the child, irrigoscopy (examination of the colon using a contrast agent), sphincterometry (measuring pressure in the patient’s anal sphincter), or examination of the vagina can be performed. Sometimes an additional examination by a gastroenterologist or pediatric surgeon is required.
Treatment appointment
Treatment depends on many factors: the medical history, the condition of the child, the results of examination and research, individual reactions of the child. If the disease that caused the abdominal pain is not particularly dangerous, the child may be at home. In more serious cases, outpatient treatment or even surgery is required.
At home, the child should be transferred to bed rest and ensure that he has sufficient fluid intake to exclude dehydration. Follow a diet, it is better to give food in semi-liquid form. Medicines without a doctor’s prescription should not be given (especially antibiotics and aspirin) and should not be carried away by traditional medicine methods (for example, uncontrolled use of medicinal herbs).
If the child has a temperature, you can give an antipyretic, for example, paracetamol-based drugs. Drug treatment is recommended if the temperature is 38 or higher, and diarrhea or vomiting lasts more than a day.
What to give a child with abdominal pain at home
Parents and guardians should carefully monitor the condition of the child and immediately consult a doctor at the first sign of danger. Especially carefully monitor the well-being of the child is required when he is in the process of recovery. It is especially difficult for parents if the child is a teenager; they have to be sophisticated so that the manifestation of their concern the child does not take for obsession and does not rebel.
Bed rest. The supine position helps to relieve a little pain in the abdomen. If you lie face down on the bed, pain from intestinal gases is less noticeable; however, the child will find the most convenient position for himself.
Diet. People can live a long time without food, but they need to drink constantly. But do not forcibly give the child a drink; it takes time to develop dehydration. With severe vomiting, the child is simply not able to retain a large amount of fluid. Usually in such cases, doctors recommend giving the liquid in small portions (about half a glass) every half hour, until the child can drink on his own. The child should avoid using colored liquids (coffee, tea), soda, milk, too salty (isotonic, sports drinks) or sweet (fruit juices) liquids.
- How to drink a child. If you give the child only water, this can lead to disturbances in the salt balance in the body. It is not necessary to give the child milk to drink, as the child’s digestive system assimilates it with great difficulty in case of pain. Therefore, doctors recommend electrolyte solutions that normalize the water-alkaline balance in the body. You can buy them without a prescription. Older children can already be given broth. If a child asks for carbonated drinks, you should choose those that do not contain caffeine. Before giving a child a drink of gas, it is worthwhile to let it out a little, so that the child can carry it easier.
- Solid food. The child himself will say when he wants ordinary food. The transition to the usual diet should start with crackers made of white bread, then bananas, baked apples, rice without seasoning, and monitor the body's response to changes in the diet.
If a child has a stomach ache, what can be given to relieve pain?
If the cause of the pain is the stomach, esophagus or small intestine, you can give your child any of the antacid drugs. Sometimes a warming compress, a heating pad on the stomach or a bath with a hot, but comfortable for the body water temperature helps. You can use paracetamol-containing medicines to relieve high fevers.
What medications should not be given to a child?
Most doctors recommend avoiding aspirin. Do not give your child antibiotics without a doctor's prescription. Also, doctors usually do not recommend resorting to self-medication methods, for example, drinking herbal infusions. If the parents nevertheless used traditional medicine methods, it is necessary to tell exactly what they gave the child at the doctor’s appointment. Some methods used in traditional medicine can affect the effectiveness of the proposed treatment. It is also better to refrain from the use of spasmolytics: they can smear the picture of the disease and make it difficult for the doctor to diagnose.
Prospects
The rate of recovery depends on the cause of the abdominal pain. If it can be detected in the early stages of the development of the disease, the overall prognosis will be favorable. If the disease is started, it can lead to complications and even threaten the life of the child. Accordingly, the sooner the parents or guardians go to the doctor, the better.
The main signs of acute respiratory viral infections are familiar to everyone: this is a runny nose, sore throat, cough, lacrimation, etc. Such symptoms provoke viral infections that penetrate the human body. Noticing at home, their child, one or several of the above symptoms, people immediately begin to take appropriate measures for the treatment of colds. However, with SARS, there is one symptom that for many seems very strange and completely incompatible with a cold - abdominal pain. Surely, many parents faced a problem when their baby complained of sharp abdominal pains, although you know for sure that he does not have an upset or any disturbance in the intestines. Why is this happening, and what solutions can be offered?
Abdominal pain in a child may occur as a result of colds
The stomach during acute respiratory viral infections in a child can hurt at almost any age, and in general, this symptom does not depend on the person’s age. Parents should be ready for such a phenomenon at any time, although when such a situation occurs in their lives, it is difficult to prepare for it, and it always becomes scary for the baby’s health.
There are many cases when pain appeared in children 3-4 years old - they complained that they had a stomach ache, they feel discomfort in this part of the body. After the tests, the doctors concluded that this was not an intestinal infection, not an upset stomach, but an ordinary cold, which caused such unpleasant symptoms.
Older children also experience pain in the abdomen with respiratory infections, so do not be surprised if the child complains of such signs, but it turns out that he has a common cold or flu.
You can not scold the child for what he feels, to say that he invented all this himself, and there should be no pain in the abdomen. The kid feels his body better, and parents are required to listen to his experiences.
At the same time, it is impossible to draw sudden conclusions, independently trying to determine the diagnosis of the disease. It is necessary to consult a specialist so that he establishes an accurate diagnosis, and can prescribe exactly the treatment that your child needs.

Abdominal pain with ARVI can occur at any age
Symptomatology
When a stomach ache after an acute respiratory viral infection in a child, it is worth paying attention to other symptoms that will help determine that this condition occurs just because of a cold or flu, and not because of an intestinal infection:
- an increase in body temperature, often a slow increase to 37.5-38 degrees;
- the presence of a runny nose;
- dry cough;
- feeling of weakness;
- inflammation of the sinuses of the nose or ear;
- nausea and vomiting.
If the child is old enough, and he can already describe his condition, you should ask him exactly where he feels pain, when there were unpleasant sensations, what he is experiencing at a given time.
Abdominal pain with acute respiratory viral infections and colds can occur for various reasons, which will be discussed later. But the main thing to remember is that such symptoms cannot be ignored.
As soon as the first signs have made themselves felt, you should immediately seek help from qualified specialists, otherwise the consequences of self-medication may be too dangerous for the health of the child.

Abdominal pain is accompanied by a runny nose, cough and other symptoms of SARS
Causes
There may be several causes of abdominal pain in acute respiratory viral infections in children. Only an experienced doctor can determine the root cause, so you should immediately seek medical help. Such a symptom may occur due to:
- The use of certain medications that cause side effects or are contraindicated in your child. That is why it is recommended to carefully read the instructions for the use of medicines, as well as consult with a doctor regarding medicines. Even seemingly harmless baby syrups can cause discomfort in the abdomen.
- The negative effects of viral infections that penetrate the stomach or intestines and damage the functioning of internal organs. Many underestimate the effect of pathogenic bacteria, although they, in turn, can cause great harm to the human body.
- A large number of snot and purulent discharge during a runny nose when a child swallows saliva along with these accumulations. The abdomen in this case may respond with the disorder.
- The temperature rises when the level of acetone rises. One of the signs of an increase in acetone is abdominal pain.
These are the main causes of abdominal pain that can occur with colds, although there are some others. Only a professional doctor will be able to accurately determine what caused this symptom in a child. Diagnosis is necessary in order to prescribe the correct treatment, so you should not avoid it.

Abdominal pain with ARVI appears, usually due to the action of viruses and bacteria
What to do?
The main question that all parents have in a similar situation is as follows: what to do now? Even if you know for sure that a cold has become the cause of abdominal pain, you need to do something to get rid of an unpleasant symptom and illness in general.
The very first step is to seek help from a qualified pediatrician, who has been working with children for years, and knows firsthand how to treat children with completely different signs of SARS.
The task of parents is to cure a cold illness in their baby, as well as to deal with the treatment of pronounced symptoms, including abdominal pain. You should not start treatment with the elimination of symptoms, as this will not lead to anything good. The child will feel lighter, but subsequently the symptoms will return, and perhaps there will be much more than before.

For abdominal pain in a child, it is urgent to seek medical help
Drug treatment
As mentioned above, with acute respiratory viral infections and abdominal pain, treatment should begin with drugs that are designed to kill viral infections.
- Candles Viferon. The tool has excellent antiviral properties and is prescribed even for the smallest children. Suppositories can be used for infectious and inflammatory ailments, as well as for severe abdominal pain due to rotavirus infection.
- Anaferon for children. The tool is intended for the treatment of diseases of the upper respiratory tract, excellently strengthens the immune system of the child. Available in tablet form.
- Interferon It is used to treat respiratory viral diseases, it is allowed to use for children almost from their birth.
- Grippferon. An antimicrobial agent that helps get rid of infections in the body, protects against flu and colds.
- Drops Derinat. Special drops in the nose, which are used for colds for the prevention and treatment of acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections.
Remember that the use of any of the above drugs must be agreed with your doctor. Many of these agents have certain side effects, so they can cause an allergic reaction, dizziness, and other undesirable effects. To avoid this, consult with a specialist.
Drugs for abdominal pain
If during a SARS the child still has a stomach ache, you can try the following drugs designed to eliminate such symptoms:
- Mezim. Normalizes the digestive tract, copes with digestive disorders caused by any reasons.
- Festal. Promotes the rapid absorption of food and their further breakdown, improves metabolism.
- Panzistal. The combined enzyme preparation, which contains components of the pancreas, normalizes the digestive process, removes pain and discomfort in the abdomen.
Before using this or that remedy, be sure to consult your doctor, because these drugs can also cause certain side effects.
Abdominal pain in a child with SARS is always an unpleasant symptom that causes a feeling of pity for your baby. During this period, the child worries about his health, experiences pain, discomfort, often cries and is capricious. However, you should not be very afraid of this symptom, especially if an ordinary cold is to blame.

After treating a cold, you can give the child Mezim or Festal to eliminate abdominal pain
Timely measures taken by parents will help to avoid serious complications and all kinds of consequences, and soon the child will feel much better.