Opisthorchiasis is a systemic disease in which many organs are affected. In the chronic course of helminthiasis, deep, sometimes irreversible morphological changes in organs and tissues are formed. Treatment of opisthorchiasis should be comprehensive and affect all links of the pathological process. With its successful implementation, the clinical manifestations of the disease are stopped or reduced, the functioning of vital organs improves and often completely restores.
Most patients are treated on an outpatient basis. With a severe course of the disease, the patient is hospitalized. When prescribing drugs for the treatment of opisthorchiasis, the patient's age, concomitant pathology, severity and clinical features of the disease are taken into account.
Treatment of opisthorchiasis is phased. First, the proper outflow of bile and pancreatic juices is ensured, anti-inflammatory, detoxification and anti-allergic treatment is carried out. Next, deworming is carried out, after which - rehabilitation (recovery stage).
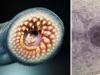
Figure: 1. In the photo opisthorchis.

Figure: 2. In the photo there is an opisthorchus suction cup located at the head end. Suction cup with cuticular spines (photo on the left). In the photo there is a sucker and a throat in the middle. View of the suction cup in a scanning microscope (photo on the right).
Diet for opisthorchiasis
The diet involves excluding fatty foods from the diet, as well as spicy, fried and smoked foods.
Recommendedeat low-fat fish and meat, yesterday's bread, crackers, vegetable soups, low-fat cottage cheese and dairy products, soft-boiled eggs and omelets, a small amount of butter and vegetable oil, cereals, fruits and vegetables, weak coffee, tea and juices.
Is prohibitedspicy, salty, sour and fried foods, fresh baked goods, legumes, sweets.
Culinary processingwhen cooking: it is recommended to steam, bake or boil food.
Meal frequency: food fractional, in small portions, 6 times a day.

Figure: 3. Diet for opisthorchiasis is an integral part of pathogenetic treatment
Treatment of opisthorchiasis at the preparatory stage
The task of the therapy of the first preparatory stage is to restore the proper outflow of bile and pancreatic juices, relieve allergic manifestations and inflammation, combat intoxication, and improve the functioning of the liver, stomach and intestines. The duration of the preparatory stage is 15 to 20 days.
Elimination of symptoms of biliary dyskinesia
If the patient develops pain in the right hypochondrium, it is necessary to establish the type of biliary dyskinesia and choose the correct treatment. With congestion (hypokinetic dyskinesia), stimulants of bile secretion are prescribed - cholekinetics and conducting blind probing procedures (tyubazh). To stimulate bile formation, reception is shown choleretics... The course of treatment for opisthorchiasis with choleretic and antispasmodic drugs is from 1 to 3 months.
Stimulants of bile formation (choleretics)
Bile production is stimulated by preparations containing bile acids, synthetic preparations, herbal preparations and hydrocholeritics.
- Bile acid preparations include: Hologon,Decholin, Allohol, Festal, Cholenzym, Digestol, Mexaza, Lyobil.
- Synthetic choleretics include: Nikodin, Tsikvalon, Oxafenamide, Holonerton.
- Herbal preparations include: Kurenar, Galstena, Flamin, Holagogum, Fumeterre, Holagol, Holaflux, Holosas.Plants: Helichrysum flowers, Corn silk, Flamin, Peppermint, Holosas, Holagol, Parsley, Holaflux, Tanaflon, Polifitohol, Kurepar, Fumeterre.
- Hydrocholeretics include mineral waters: "Essentuki" No. 17 (strongly and slightly mineralized), "Izhevskaya", "Jermuk", "Naftusya", "Smirnovskaya", "Arzni" and "Slavyanovskaya".
Biliary stimulants - ( cholekinetics)
Cholekinetics help to contract the gallbladder and relax the sphincter of Oddi. These include: Xylitol, Sorbitol, Magnesium sulfate, Carlsbad salt, Berberine, Alcohol tincture of barberry leaves, Decoctions of tansy and Sunflower oil.

Antispasmodics
- Preparations containing drotaverine: Drotaverine and No-shpa.
- Expands blood vessels and relieves spasm of smooth muscles of the gallbladder, bile and pancreatic ducts, stomach, intestines, kidneys and bronchi Platyphyllin.
- As an antispasmodic agent, preference should be given to selective drugs containing mebeverine: Mebeverin, Mebeverin hydrochloride, Mebespalin retard, Dutan, Duspatalin, Talinda retard, Sparex, Niaspam.They selectively act on the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract - they reduce the tone and reduce their contractile activity, do not cause side effects, and actively affect the sphincter of Oddi.

Figure: 5. The photo shows a mass of eggs in the uterus of opisthorchus, located in the biliary tract.
Hepatoprotectors

Figure: 6. Damage to the liver with opisthorchiasis.
Enzyme preparations
Enterosorbents effectively bind and remove toxic substances from the body. Thus, the clinical manifestations of food poisoning and diarrheal syndrome are weakened. Their use helps to restore the functions of the gastrointestinal tract and the immune system.
For digestive disorders, enzyme preparations are prescribed: Pancreatin, Mezim forte, Digestal, Digestal forte, Festal, Panzinorm forte, Creon, Penzital, Pangrol and etc.
Allergy treatment
The waste products of opisthorchs (toxins) in the host's body cause sensitization (hypersensitivity) and the development of an allergic reaction. It is allergosis that comes to the fore in the pathogenesis of the development of the acute stage of opisthorchiasis. It manifests itself as granulomatous hepatitis, pancreatitis, antigenic pneumonitis and eosinophilic infiltrates in a number of other organs and tissues.
- Enterosorbents effectively bind and remove toxic substances from the body. For opisthorchiasis, enterosorbents of different groups are used: Activated carbon, Polysorb, Smecta, Neosmectin Enterodes, Enterosgel, Enterosorb, Multisorb and etc.
- From antiallergic drugs, antihistamines of the 2nd and 3rd generations are used: Lomilan, Claridon, Claritin, LauraHeksal, Zyrtec, Rupafin, Telfast, Trexil. The drugs of this group are used in the acute phase of the disease and, if indicated, in the chronic phase and the rehabilitation period.

Figure: 7. Rash with lesions of the digestive system.
Anti-inflammatory therapy
With the help of an oral sucker and cuticular spines, opisthorchis are fixed on the mucous membrane of the gallbladder, bile ducts and pancreatic ducts, which leads to mechanical damage and disruption of their blood supply. The walls of the ducts become inflamed, and multiple bleeding erosions appear on them. As anti-inflammatory drugs for opisthorchiasis, groups of penicillins, cephalosporins or macrolides are used.

Figure: 8. In severe opisthorchiasis, liver function is disrupted, yellowness of the sclera and skin appears.
Treatment of opisthorchiasis at the stage of deworming
After the preparatory period, the patient is prescribed anthelminthic drugs. The effectiveness of specific chemotherapy depends on the quality of the preparatory stage.
Opisthorchiasis pills
For the treatment of opisthorchiasis, drugs such as Praziquantel, Chloxiland Albendazole... The most effective of these are preparations containing praziquantel - Praziquantel and Biltricide.Analogue Praziquantela domestic drug Azinox proved to be highly effective and in recent years also began to be used in the treatment of trematodes.
Praziquantel and Biltricide in the treatment of opisthorchiasis
Conditions for prescribing drugs:
- Before starting the treatment of opisthorchiasis, it is necessary to check the functional state of the kidneys and liver. With insufficient work of these organs, the dose of drugs is halved.
- Praziquantel and its analogs are prescribed no earlier than 3 weeks after the onset of the disease and the level of eosinophilia in the blood is no more than 20%.
Treatment of opisthorchiasis is best done in a hospital.
Pharmacological action of the drug
The death of opisthorchis when exposed Praziquantela and Biltricide is associated with the development of spastic paralysis in them, which arises as a result of an increase in the permeability of cell membranes for calcium ions, which in turn leads to a reduction in the muscles of helminths.
Doses and methods of administration
Biltricide and Praziquantel used in a dose of 50 to 75 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day for 1 to 3 days. With a single dose, the pill is taken in the evening. With multiple (sparing technique) - during the day with an interval of 4 to 6 hours. The tablets are taken orally before or during meals, are not chewed, washed down with water. On the second day after taking the drugs, duodenal or blind intubation is prescribed. This will make it possible to evacuate the decay products and vital activity of opisthorchus. Blind probing should be done with caution in children.
Interaction with other drugs
While taking from Dexamethasonethere is a decrease in the concentration of anthelmintic drugs in the blood plasma.
Side effect
Appointment Biltricide or Praziquantelside effects may occur: increased body temperature, headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, pain in the abdomen and right hypochondrium, diarrhea, pruritus, urticaria, rarely lethargy and disorientation in space.
Adverse reactions are usually short-lived and disappear quickly. The most pronounced and long-term side reactions with massive helminthic invasion.
Contraindications
The first trimester of pregnancy, children under 4 years of age, hypersensitivity to the drug and ocular cysticercosis are the main contraindications for taking Biltricide or Praziquantel. The drugs are contraindicated in persons with severe neuropsychic pathology. During the period of treatment, you should stop breastfeeding and work associated with a quick concentration of attention. With caution, drugs should be prescribed to persons with diseases of the kidneys, liver and heart, as well as to elderly and senile persons.
Due to the high toxicity, anthelmintic drugs are used only as directed and under medical supervision. Do not self-medicate!

Figure: 9. Biltricid and Praziquantel are anthelmintic drugs.
Treatment of opisthorchiasis during the recovery period

Figure: 10. In the photo opisthorchis. An adult feline fluke has a lanceolate body - flat and elongated. Its length is 8 - 18 mm, width is 1.2 - 3.5 mm.
Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment (deworming)
The control of the effectiveness of deworming is carried out using a microscopic method for examining feces or duodenal contents 1, 3 and 6 months after treatment, three times in each of the indicated periods.

Figure: 11. Eggs of opisthorchus in feces.
Episthorchiasis prognosis
In most cases, the prognosis of the disease is favorable. The prognosis worsens with the development of serious complications from the bile ducts and pancreas - bile peritonitis, acute pancreatitis and the development of primary liver cancer.
Features of the treatment of chronic opisthorchiasis
In chronic opisthorchiasis, deep morphological changes in the organs are formed. Patients with a chronic course of opisthorchiasis are shown to carry out complex therapy, the purpose of which is to sufficiently restore the affected organs and prepare the patient for anthelminthic treatment. The completion of the treatment process is the implementation of rehabilitation (recovery) measures.
Preparatory stage
In chronic opisthorchiasis, the course of preparatory therapy lasts 2 to 3 weeks. Therapeutic measures are aimed at improving the functioning of the liver and pancreas, stomach and intestines, eliminating the symptoms of biliary dyskinesia, allergic reactions and toxicosis.
Rehabilitation therapy

Figure: 12. In the photo opisthorchis grown in laboratory conditions (photo on the left) and opisthorchis and caudate larvae (photo on the right).
Prevention of opisthorchiasis
Prevention of opisthorchiasis is multifaceted. It includes measures aimed at protecting water bodies from fecal contamination, observing fish cooking technology, health education and health promotion.
Sanitary and preventive measures:
- Protection of freshwater reservoirs from contamination with fecal masses of people and animals. Do not allow sewage waste, household waste, fish production waste and waste from water transport latrines to enter them.
Carrying out measures for the destruction of mollusks.
- Compliance with sanitary-technical rules in production.
- Compliance with the sanitary and anti-epidemic regime in organized teams.
Treatment and preventive measures:
- Identification of persons infested with opisthorchias.
- Carrying out a complex of therapeutic measures.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
Particular attention should be paid to water transport workers, fishermen and coastal residents.
Health education and health promotion
Health education of the population is carried out using memos, lectures, individual conversations, radio and television appearances.
Personal prevention:
- do not drink water from stagnant bodies of water;
- do not eat unwashed greens, especially if they are watered from standing water sources;
- do not eat raw and semi-raw fish, do not taste minced fish or other fish product;
- after working with fish, thoroughly wash the knife and cutting board.
Do not feed raw fish to pets.

Figure: 13. Raw and half-raw fish can be a source of opisthorchiasis.
What types of fish are affected by opisthorchiasis
The infection of carp fish is different. In some cases, this figure reaches 100%. The maximum of infected fish is recorded in water bodies located near settlements, in commercial lakes and dry river beds (oxbows).
The carp genus includes dace, carp, bream, roach, ide, roach, carp, blue bream, crucian carp, tench, bleak, spike, rudd, chebak, ram, minnow and others.
Sometimes there are whitefish species infected with opisthorchis larvae - vendace, muksun, cheese and shchekur. There are cases of carriage of helminthiasis in fish living in the same reservoir with carp fish - perch, pike, burbot, smelt and pike perch.
Carp fish are one of the most important fisheries in our inland waters.
How fish infestation is detected
To identify fish infected with opisthorchiasis metacercariae, it is necessary to make an incision along the dorsal fin with a scalpel, cut off a skin flap and make a thin section of muscle tissue. Metacercariae are clearly visible under a magnifying glass with a magnification of 10 - 20 times.

Figure: 14. Opisthorchis enter the human body and carnivorous animals in the form of metacercariae located in muscle tissue and adipose layer. Metacercariae is located in a rounded cyst - a capsule in the form of a mobile larva.
Rules for processing freshwater fish at home
Freezing
The duration of freezing fish at a temperature of 28 º C is 32 hours, at a temperature of 35 º C - 14 hours, at a temperature of 40 º C - 7 hours.
Cooking fish
Cook fish in a piece should be at least 20 minutes, dumplings with minced fish - at least 5 minutes from the moment of boiling.
Frying fish
Whole small fish and fish cakes are fried for 15 to 20 minutes. Large pieces weighing up to 100 grams are fried for 20 minutes.

Figure: 16. In well-fried fish, opisthorchis are absent.
Baking with fish and minced fish
Culinary products with fish and minced fish are baked in the oven for at least 50 - 60 minutes.

Figure: 17. Pies with fish should be baked for at least 50 - 60 minutes.
Salting fish
The fish is salted in a strong saline solution (the amount of salt should be at least 15 - 20% of the weight of the fish) for 14 days. Large fish are salted for at least 40 days, fish up to 25 cm in length are salted for 21 days, small fish for at least 10 days.

Drying fish
There are two ways to dry fish:
Method 1: salting (for 10 kg of fish, 2 kg of salt) for 2 weeks, then soaking and drying (to taste).
Method 2: salting (for 10 kg of fish, 2 kg of salt) for 3 days, then drying for 3 weeks.
Small species of carp fish (dace, roach) are salted within 2-3 days, followed by drying for 3 weeks.

Figure: 19. Drying fish.
Smoking fish
The hot type of smoking is carried out for 2 - 2.5 hours at a temperature of + 70 - 80 ° С.
The cold type of smoking is carried out after strong salting (for 10 kg of fish 2 kg of salt) for 2 weeks or freezing for 2 days at a temperature of 28 ° C or 10 hours at a temperature of 35 ° C.

Figure: 20. Smoking bream (left photo). Ready-made cold smoked bream (photo on the right).
The absence of low-temperature chambers at fish processing plants is one of the factors in the spread of infection.
Hello. About two years ago, my son and I contracted opisthorchiasis. I have symptoms: mostly only allergies - itching, urticaria, my son - allergies, gastrological problems, temperatura. Diagnosed by feces in the MCC NSMU. We underwent a course of treatment with biltricide in 1 infectious diseases hospital in Novosibirsk, with preparation. Duodenal intubation after biltricide was not prescribed, but a course of 3 months was prescribed. with choleretic and mineral water and sorbitol, all appointments were fulfilled, the symptoms disappeared. Three months later, a blood test was carried out in the same place at the MCC NSMU (on their advice), opisthorchiasis was not found.In March 2016, the son had problems with digestion, turned to a gastroenterologist, said a possibly under-treated opisthorchiasis, prescribed hofitol, eksorsol, lactofiltrum, after eksorsol duodenal probing - opisthorchias were not found, the symptoms were significantly weakened. I started to experience itching mainly on my hands and feet, but less pronounced than 2 years ago. The main question is which method is the most reliable for confirming or denying opisthorchiasis: duodenal intubation or a blood test for opisthorchiasis IgM / IgG / CEC, or both.? Thanks in advance.
Result: positive feedback
10 +
Unpleasant, but effective
Result: positive feedback
Effectiveness is dose dependent
Benefits: With the right dose, effective
Disadvantages: Severe side effects
Result: negative feedback
Has not completely cured
Disadvantages: Did not completely get rid of helminths, caused vomiting and diarrhea, undeservedly expensive
Result: positive feedback
I like this
Benefits: Heals in 2 days, effective, available for free
Disadvantages: Preparation is needed before treatment, there may be side effects
A huge plus of Biltricid is that it heals opisthorchiasis in just two days. The biggest disadvantage of the tool is that it cannot be used without preparation and does not make sense, because there simply will be no effect. I personally did everything right - I went to the infectious diseases hospital, where they gave me choleretic drugs for a week, passed tests, and the next week I took Biltricide - they gave it to me for free, so if you have the opportunity, go to the hospital, and for You do not need to pay for the medicine, and you will be under supervision. Although I personally did not need supervision - I drank all the prescribed pills, felt nothing, went to bed. The next day there were no problems either - except that my head was spinning a little and my head was noisy, but otherwise everything was fine. After taking the pills, I spent another week in the hospital - the same choleretic and droppers. And then there was a reaction of the body to intoxication - I was sprinkled all over with acne, all the skin began to itch, my eyes were constantly itching, watering and a sore throat. This lasted quite a long time - about a month and a half, but then everything returned to normal. Now I check it every six months - so far everything is clean.
1A.L. Korkin, V.V. Khryachkov
19 healthy people and 33 patients with opisthorchiasis and cholelithiasis were examined. A comparative assessment of some parameters of cholesterol, pigment, protein metabolism in the gallbladder and hepatic portion of bile in the examined patients before and after therapy with biltricide and ursosan was carried out. It was revealed that in patients with opisthorchiasis and cholelithiasis, in effective terms after monotherapy with biltricide, there is a significant excess of the concentration of indirect bilirubin, cholesterol and protein in the gallbladder bile compared with healthy people, which indicates the preservation of residual effects with a significant improvement in pigment metabolism and a decrease in the lithogenic properties of bile ... The inclusion of ursosan in the preparation and implementation of anthelmintic therapy makes it possible to achieve the highest hypolithogenic state of the gallbladder portion of bile within an effective time frame after biltricide therapy.
The chronic phase of opisthorchiasis, often asymptomatic, with normal or minimal changes in liver biochemical samples, is characterized by functional changes in the biliary system, the biochemical composition of bile in the form of a decrease in phospholipids, an increase in cholesterol and total bilirubin in the gallbladder and hepatic portion of bile. Some authors have noted a decrease in cholesterol in the gallbladder portion of bile. All this is considered as an increase in the lithogenic properties of bile in opisthorchiasis, increasing the risks of developing cholelithiasis.
In the light of the latest understanding of lithogenesis, a drug solution to this problem is considered in the development of new strategies for the prevention and treatment of early stages of cholelithiasis.
The aim of this work was to study the level of bile lithogenic factors in patients with opisthorchiasis and cholelithiasis at an effective time after chemotherapy with biltricide and ursosan.
52 patients were examined. The first group consisted of 19 people in whom opisthorchiasis was not detected according to the results of a coprological study and during duodenal intubation. In this group, no pathological changes in the hepatobiliary system were revealed according to the results of clinical and biochemical blood tests and ultrasound of the liver, biliary system. The second group was left with 20 patients with opisthorchiasis and stage 2 cholelithiasis. In this group, the study of the biochemical composition of bile was carried out before biltricide therapy and 2 months after therapy with this drug. The third group (13 patients) consisted of patients with opisthorchiasis and stage 2 cholelithiasis before treatment with biltricide and ursosan and 2 months after therapy with these drugs.
In groups 2 and 3, before treatment with biltricide and ursosan, opisthorchiasis invasion was verified based on the results of scatological studies and duodenal intubation. The second stage of cholelithiasis (the stage of microlith formation) was verified in these groups according to the results of ultrasound of the gallbladder.
Biltricid was prescribed to patients of groups 2 and 3 at the rate of 60 mg per 1 kg of patient weight in 3 divided doses during the day. Ursosan was prescribed to patients of group 3 2 weeks before biltricide therapy and within 2 months after it at the rate of 10 mg per 1 kg of patient weight per day in 2 daily doses: morning and evening.
Determination of the level of cholesterol, bilirubin, total protein, albumin was carried out by a unified method "by the end point" on an automatic analyzer Synhron CX 5 Delta from Bekcman Culter. Determination of protein fractions was carried out by electrophoresis on agarose gel on an electrophoretic system Densitometer System Appraise from Bekcman Culter. Determination of the activity of alkaline phosphatase was carried out by an optimized kinetic method using 2-amino-2 methyl-1-propanol buffer on an automatic analyzer Synhron CX 5 Delta from Beksman Culter.
Numerical data obtained in the course of the study are subjected to statistical processing using Microsoft Excel and Stat-Soft.
In the effective terms of therapy with biltricide, there is a significant decrease in cholesterol levels in the hepatic and cystic portion of bile, which, however, exceeds the level in bile in healthy people (see Table 1).
Table 1.Indicators of cholesterol (μmol / L), cholesterol-phospholipid ratio, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase (μmol / L), total protein and protein fractions in bile (g / L) in patients with opisthorchiasis and cholelithiasis after therapy with biltricide and ursosan (M + σ )
|
Indicators |
before therapy |
Group 2 after therapy |
before therapy |
Group 3 after therapy |
|
|
Portion B |
|||||
|
Cholesterol |
|||||
|
Xc / phospho-lipid |
|||||
|
General |
|||||
|
Indirect bilirubin |
|||||
|
Alkaline phosphatase |
|||||
|
Total protein |
|||||
|
Albumen |
|||||
|
α1-globulin |
|||||
|
α2-globulin |
|||||
|
β-globulins |
|||||
|
γ-globulins |
|||||
|
Serving C |
|||||
|
Cholesterol |
|||||
|
Xc / phospho-lipid ratio |
|||||
|
Total bilirubin |
|||||
|
Indirect bilirubin |
|||||
|
Alkaline phosphatase |
|||||
|
Total protein |
|||||
|
Albumen |
|||||
|
α1-globulin |
|||||
|
α2-globulin |
|||||
|
β-globulins |
|||||
|
γ-globulins |
A decrease in the cholesterol-phospholipid ratio in hepatic and gallbladder bile in the effective periods of biltricide therapy indicates a decrease in the lithogenicity of bile.
In addition, in the effective terms of therapy with biltricide in group 2, the state of bilirubin metabolism improves in the form of a decrease in the level of total and indirect bilirubin in bile compared to the initial level (see table 1). However, the excess of the concentration of indirect bilirubin in the hepatic and gallbladder bile even in effective terms after biltricide therapy in group 2 compared with group 1 indicates the preservation of residual changes with an improvement in pigment metabolism (p<0,05; см. таблицу 1).
When studying the indicators of protein metabolism in group 2, a significant decrease in total protein in the hepatic portion of bile was revealed in the effective period after biltricide therapy compared to the initial level (see table 1).
The excess of the arithmetic mean of γ-globulins in the hepatic and gallbladder bile in group 2 compared with group 1 indicates the preservation of the intensity of immunological reactions during the effective periods of biltricide therapy. Although the decrease in the level of γ-globulins in bile in group 2 compared with the initial level is generally considered a positive trend (see table 1).
Despite the decrease in the level of albumin in the gallbladder bile in group 2 during the effective periods of biltricide therapy compared to the initial level, it remains rather high, exceeding the value of the indicator in group 1, being an important factor of increased lithogenic activity in these patients (p<0,05; см. таблицу 1).
In effective terms after therapy with biltricide and ursosan, patients of group 3 showed the lowest values \u200b\u200bof cholesterol, bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase in bile compared with patients of group 2 (see Table 1). When comparing the arithmetic mean of these indicators and analyzing the results of the Mann-Whitney test in groups 1 and 2, there were no statistically significant differences in the effective periods of therapy with biltricide and ursosan (p\u003e 0.05; see Table 1).
When comparing the cholesterol-phospholipid ratio in the gallbladder and hepatic portion of bile, in the effective terms after the therapy, the lowest values \u200b\u200bof the indicator were observed in the group of patients of group 3 compared with group 2.
When studying the fractions of bilirubin in bile within effective terms after therapy, patients of group 3 have the lowest values \u200b\u200bof indirect bilirubin compared with groups 1 and 2 (see Table 1).
Evaluation of the content of total protein and its fractions in bile at an effective time after biltricide therapy in patients of group 3 reflects the patterns characteristic of group 2. However, we found that a feature of group 3 is a lower level γ -globulins in bile during effective periods of therapy, which does not differ statistically significantly from the level of the indicator in group 1 (p\u003e 0.05; see table 1).
Conclusions:
- In effective terms after biltricide therapy, a decrease in the lithogenic properties of bile was revealed, which has a significant but mediated mechanism associated with the resolution of intraductal biliary cholestasis and a decrease in inflammatory and immunological reactions in the biliary duct system.
- In effective terms after biltricide therapy, a significant excess of the concentration of indirect bilirubin, cholesterol, and protein in the gallbladder bile was revealed in comparison with healthy people, which indicates the preservation of residual effects with a significant improvement in pigment metabolism and a decrease in the lithogenic properties of bile.
- The inclusion of ursosan in the preparation and implementation of anthelmintic therapy makes it possible to achieve the highest hypolithogenic state of the gallbladder portion of bile during the entire period after biltricide therapy and to achieve lower levels of these parameters within an effective time frame after deworming.
- Ursosan has no significant effect on the intensity of inflammatory processes and the level of indirect bilirubin in bile in patients with opisthorchiasis.
- The combined use of biltricide and ursosan makes it possible to achieve lower indicators of bile lithogenicity within an effective time frame after biltricide therapy.
08.02.2010, 13:01
Hello! My name is Maria.
I am 22 years old, weight 53 kg, height 165 cm.
I was treated with biltricide 4 days ago (6 tablets).
When I was discharged, they told me to do tyubazh, and take choleretic for 2 weeks a month for 3 months. They said you can drink herbs or pills allohol, alfit, odeston. And then they also advised the dietary supplement "Ekorsol", which includes aspen bark and marsh hodgepodge, which have a kind of "anti-opisthorchiasis effect". I was told that these substances are capable to some extent of fighting against opisthorchis ... Well, if suddenly they remained after biltricide, which may be, since when probing opisthorchus they found three bile fences in three fences, and said that this is a lot.
Should you buy Ecosol? If I buy regular wasp bark, do I get the same effect? And does aspen bark really have such an effect?
08.02.2010, 15:08
No, none of these drugs are recommended for the treatment of opisthorchiasis. By the way, I would give 1 more pill. Eggs were found in bile prior to treatment? After treatment, was control probing performed? Was the level of liver enzymes measured after treatment?
08.02.2010, 16:45
Yes, I am not quite clear about it ...))
Probing took place BEFORE treatment, 2 months ago. In the clinic, the infectious disease doctor said that there were eggs in three bile samples, and this is a bit too much, so she said that biltricide treatment may not be 100% successful.
After a month and a half, I went to the hospital, there is a preparatory period for 5 days (physiotherapy with a beam for the outflow of bile, allochol after eating, once a tube with magnesia). On the 6th day, I took 2 tablets of biltricide with an interval of 4 hours. She tolerated the medicine normally. The next two days - tyubazh with magnesia, after which I returned home with recommendations from the attending physician (head of the department), described in the first message.
During this week in the hospital I passed a general urine test, feces, a general blood test, a biochemical blood test. I did not see the results in my eyes, but the doctor told me that the results are good, without any complaints, there is even nothing to discuss :). On the last day before discharge, I donated feces, everything is fine.
Control probing was recommended to be done in 2 months.
I haven’t heard anything about the level of liver enzymes ... And what kind of analysis is it checked?
The doctor's recommendations on taking choleretic drugs, as I understand it, did not relate directly to treatment, but something like a recovery period to cleanse the body of corpses :) And then - control probing.
08.02.2010, 17:05
Clear. No, all these dietary supplements are not related to the competent treatment of opisthorchiasis. Do not forget to pass control soundings in time (three times with a break a week in case of a negative result). There is a relatively recent topic in the section about aspen bark.
08.02.2010, 20:35
I got acquainted with the topic about bark!
By the way, I was lying in the ward of the city infectious diseases hospital in Novosibirsk, about 55 steps from Tolokonskaya's office;) But this is so, by the way :)
08.02.2010, 20:50
Honestly, it won't. Moreover, allochol contains ready-made bile, and does not at all urge it to go out: D
09.02.2010, 05:16
Ahh, that's how it is :)
Thank you, Elena Evgenievna, for clarifications and recommendations!
15.02.2010, 19:15
Elena Evgenievna, about a week after taking biltricide, a rash appeared - rare red seals that constantly itch. I used to have such, but not always and not always. And then they just poured everything out at once and wherever possible :) There are 15 pieces all over the body. Does this happen? Doctors said (before treatment) that the rash is a manifestation of opisthorchiasis. Can intoxication of the body appear in this way after treatment?
P.S. I'll go to the doctor the day after tomorrow.
15.02.2010, 23:10
Yes maybe. After deworming with opisthorchiasis, a long recovery period follows, a return of symptoms without reinvasion is possible. In such cases, symptomatic treatment is prescribed.
25.01.2011, 11:37
Hello!
Almost a year ago she underwent treatment with biltricide. But ... as a real Russian person, I did not find time to bring everything to the end * I spread my hands with a guilty look * :)
As a result, not a single control probing after treatment, not a single visit to a therapist / infectious disease specialist. By the way, now there is no infectious disease specialist in our clinic :(
A month ago, a rare rash started again, red seals, itchy. Nothing else worries.
There is no doubt that it is necessary to check again by probing.
My question is this: control probes after treatment of opisthorchiasis are needed to torment a person, but to reassure the doctor that the treatment has helped; Or does it have a healing effect?