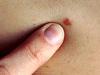
Basalioma of the skin is considered a fairly common pathology among Europeans. This type of oncology is more common in older people. The most common is the basal cell carcinoma of the face. Radiation therapy is considered the most effective method for eliminating this type of skin cancer. Let's consider in more detail the main methods of treatment, removal, complications, side effects that radiation therapy can provoke for basalioma.
Basal cell carcinoma experts refer to the group of borderline cancer. The growth of education occurs deep into the tissues, and the lump (depending on the type of oncology) can occupy a large area on the skin, take the form of an ulcer. Initially, the tumor appears on the basal layer of the epidermis. If you do not treat basal cell carcinoma for a long time, it will spread to cartilage and bone.
More often, this type of oncology develops in the dermis of the face and neck. Basal cell carcinoma can also appear in other areas that are negatively affected by aggressive factors. The most dangerous are basal cell carcinomas in the area of \u200b\u200bthe wings of the nose, on the ears, near the eye.
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma through the use of radiation therapy is possible at any stage of the disease. But now I use it less often because of the effectiveness of such modern techniques as laser and radio wave therapy.

The initial stage of basal cell carcinoma can be eliminated with medication or with minimal surgical intervention. In order for basalioma therapy to pass faster and easier, it is necessary to detect the disease at the initial stages of its development.
Radiation therapy for basalioma is indicated in the following cases:
- a tumor with a very large size;
- localization of a malignant formation in an area that is considered difficult to access;
- age (over 65 years old);
- penetration of oncology deep into the skin, into cartilaginous, bone tissue;
- the patient has diseases that are a contraindication to other therapeutic methods.
Radiation therapy is used in the complex treatment of oncology.
Ionizing effect may be required after surgery if it is impossible to completely eliminate the abnormal basalioma cells. Also, exposure to rays helps to reduce pain and other signs of the disease.
Radiation therapy methods
Radiation therapy is effective due to the effect of ionizing rays on the cell's DNA. Y-irradiation destroys the DNA of the pathological cell, which makes it unable to divide, which means that the spread of basalioma stops.
The primary target of therapeutic radiation is considered to be cells that are rapidly dividing. Also, Y-rays act on healthy tissues, provoking various consequences of basal cell carcinoma treatment carried out by this method.

Contact irradiation with isotopes of cobalt (Co60), iridium (Ir92), radium (Ra226) is carried out in such a dosage that could destroy malignant cells and prevent their further multiplication. The therapy is carried out using applicators made of plastic material. They are prepared for each patient individually.
A plate (1 cm thick) is placed in boiling water, applied to the diseased area of \u200b\u200bthe dermis... This applicator is modulated, giving the plate a relief of the skin. Radioactive substances are applied on top of the plate, protection in the form of a lead plate. Passing through the tissues, the radiation intensity decreases. Therefore, this method of eliminating basal cell carcinoma will not harm the internal organs.
Close-focus therapy, which is performed from a distance of less than 7.5 cm, requires the use of power in the range of 10 - 250 W. Changing the power changes the depth of the impact, which is represented by several millimeters and reaches 7 - 8 cm.
Beams are focused by means of a tube. The area of \u200b\u200bthe dermis to be irradiated is limited by means of filters made of different metals (brass, aluminum). The thickness of these filters is up to 3 mm. The level of absorption of rays by tissues is influenced by the stage of development of oncology, the state of the patient. Taking these features into account, the oncologist selects the number of sessions individually.
A feature of β-irradiation is the use of radioactive isotopes of such substances:
- phosphorus (P32);
- thallium (TI204).
Before exposure to the rays inside the basalioma, the doctor injects colloidal solutions of the following metals:
- silver (AG188);
- gold (Au111).
These solutions are administered by a specialist in the form of special granules, which are initially processed with catgut threads.
According to the reviews of oncologists, it is rather difficult to perform this method of irradiation, and not all clinics have unique equipment for its implementation. The described method of treatment is used to eliminate those forms of basal cell carcinoma that are resistant to other methods of radiation exposure.
What is the risk of basalioma irradiation?
In any case, the consequence of radiation treatment for basalioma is damage to healthy cells located in the tissues surrounding the tumor.

Following the rules of the procedure is not able to prevent damage to healthy tissues by rays.
The strength of the sensitivity of the epidermis to radiation is influenced by many factors:
- overweight (obese patients have a more susceptible dermis);
- localization of oncology. The dermis of the anterior surface of the neck will be more delicate, sensitive to rays. The skin of the back of the head, wings of the nose, etc .; is considered coarser;
- age-related changes;
- air temperature. Due to the increased blood supply in the heat, the likelihood of complications increases;
- the permeability of the epithelium increases in the presence of scratches, cracks.
Side effects during radiation exposure
Most of the patients treated with radiation therapy for basal cell carcinoma do not develop systemic consequences. Experts explain the manifestation of such effects by the reaction of the dermis. It is represented by epidermis.
During each procedure, the following consequences appear on the epithelium:
- redness;
- edema;
- itching.
In the course of therapy of basalioma with rays, these symptoms are more pronounced. They become brightest by the 3rd week of the course. Such consequences disappear after 1 - 1.5 months after the course of treatment for basal cell carcinoma ends. To reduce their severity, experts recommend the use of glucocorticoid ointments ("Sinaflan", "Hydrocortisone", "Prednisolone").

Minor ulcers and crusts may also appear. They indicate the development of radiation dermatitis, which will pass at the end of the therapeutic course.
The following signs indicate the development of skin changes:
- violation of pigmentation;
- the formation of "stars";
- the disappearance of the superficial pattern on the skin;
- peeling, increased dryness.
If oncology has arisen near the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth, there is a possibility of developing inflammation (mucositis). This pathology is accompanied by burning, dryness of the dermis, soreness after touching. This consequence is considered very rare. With radiation exposure to the basalioma, localized in the eye area, there is a risk of recurrent conjunctivitis.
Long-term complications that may appear after radiation
Radiation therapy can provoke not only immediate consequences, but also long-term complications. Exposure to radiation contributes to the thinning of the skin, the manifestation of the vascular network. After a year, one and a half after irradiation, lighter, darker zones of the epithelium may appear. The brightness of such manifestations depends on the duration of the previous therapy, the radiation dose received by the skin, the area of \u200b\u200bexposure.
Radiation ulcer is considered a more dangerous consequence of the described method of treatment. It is triggered by the action of radioactive isotopes on the microcirculation of the vessels located under the epidermis layer. The likelihood of an ulcer increases in proportion to the depth of penetration of the cancer, the strength of the radiation.
The most dangerous consequence of basal cell carcinoma therapy is the development of squamous cell carcinoma, which is considered a more dangerous pathology than basal cell carcinoma. Therefore, experts do not recommend radiation therapy for those under 50.... The considered method of treating basalioma should not be carried out in the presence of a relapse of the disease.

The effects of radiation therapy in the hairy area of \u200b\u200bthe skin are accompanied by hair loss. Gradually the hair grows back, but it is not as strong as it used to be. The scalp is characterized by a faded color, increased fragility, and a lack of healthy shine.
If basalioma localized near the eyes was treated, there is a likelihood of developing such consequences of therapy as cataract. Scientists have not yet been able to establish a threshold dose for irradiation of the lens, so oncologists do not know how high the risk of developing such a consequence as cataract is.
Another consequence of basalioma therapy is scarring.
This consequence, manifested after exposure to radiation, limits the mobility of muscle fibers, negatively affecting facial expressions. In order for the muscles to retain their mobility, as well as to prevent contracture (immobility provoked by scars), experts recommend performing active, passive exercises in the area of \u200b\u200bradiation exposure. Also, doctors note changes in the functioning of the sebaceous, sweat glands.
After the redness caused by radiation therapy disappears, patients are mostly satisfied with the cosmetic result. But after a few years, the scars become coarser and more noticeable.
How to relieve side effects after radiation therapy
As a prophylaxis of radiation dermatitis, treatment of the epidermis surrounding the basal cell is considered with such means:
- "Petrolatum";
- a mixture of such medicines "Shostakovsky's balm" + vegetable oil;
- "Methacyl emulsion".
Doctors recommend these measures to be applied after the first radiation therapy procedure. If the ulcer does appear, everything must be done to prevent bacterial inflammation from starting. For this purpose, lotions with such solutions (dioxidine, silver) are placed on the irradiated area of \u200b\u200bthe epidermis.
The following gels help speed up wound healing after basalioma:
- "Iruksol".
- Solcoseryl.
- "Methyluracil ointment".
- Actovegin.
To prevent the consequences after radiation therapy, manifested in the form of mucosal lesions, washing, rinsing with decoctions of herbs (chamomile, sage is used), chlorhexidine will help.

It is necessary to treat the defeat of the conjunctiva with antibacterial drops. The sun's rays on the dermis can provoke inductive edema, which is treated with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs. Ascorbic acid, vitamin P help to prevent such a consequence of therapy as pigmentation.
Prevention of complications
Before conducting radiation therapy for basal cell carcinoma, doctors must conduct a thorough examination, collect anamnesis, and send them for diagnostics to detect concomitant diseases. Having all the necessary information, the doctor correctly calculates the dosage, duration of the procedure, and the frequency of radiation sessions. This helps to reduce the risk of the effects of radiation therapy.
Considering the size of the basal cell carcinoma, a specialist in the process of performing radiation therapy capture several centimeters of healthy tissue (1 - 2 cm)... This is considered necessary to prevent the re-development of basal cell carcinoma in this zone.
To reduce the likelihood of developing the consequences of radiation therapy used to eliminate basal cell carcinoma, lead plates are used. In these products, holes are made that correspond to the shape of the basal cell carcinoma. This plate is applied to the dermis during each procedure. Before each exposure, the doctor notifies the patient that the skin should be protected from damage. You can reduce the likelihood of consequences after exposure if you follow all the doctor's recommendations:
- Protect the epidermis from direct sunlight. Solarium is not allowed. It is advisable to walk on the street in clothes with long sleeves. The skin of the face should be covered with a wide-brimmed hat. To protect the open areas of the dermis from the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation, products with a high SPF level should be applied.
- It is important to carefully perform hygiene procedures so that the marks with which the doctor marked the area of \u200b\u200bradiation exposure are not washed off.
- It is forbidden to rub, massage the epidermis that has been exposed to rays. the use of mustard plasters, cans, treatment with alcohol solutions, antiseptics is also contraindicated, if the doctor has not prescribed such procedures.
- It is forbidden to use heating pads, compresses on the area of \u200b\u200bexposure to rays.
- Before using again personal hygiene products (soap, shower cream-gel) with fragrances, you should consult your doctor.
- Before carrying out radiation therapy in order to eliminate basal cell carcinoma, it is necessary to remove decorative cosmetics 4 hours before the procedure.
- Limit visits to the pool, bath.
Radiation therapy is considered a very heavy burden on the body. Accordingly, any unusual consequences in the area of \u200b\u200bthe irradiated dermis require contacting a specialist for help. In order for the consequences of the therapy of basalioma to be milder, all the recommendations of the oncologist must be followed. It is also worth consulting with him regarding changes in nutrition, climate.
ВreastCare.ru - 2008
The most common radiation elicits a reaction from the skin. This is manifested by discomfort in the irradiated area. In most cases, the skin reaction to radiation manifests itself as a sunburn, in the form of redness of the skin area, itching, burning sensation, soreness and sometimes peeling. But unlike sunburn, the skin's response to radiation occurs gradually and usually in some areas.
Skin reactions during radiation therapy
During radiation therapy, the first thing you may notice is a change in skin color from pink to red. Moreover, some areas of the skin may be more intensely colored: this is the area near the armpit, the upper inner part of the breast and the fold under the mammary gland. Skin reactions can be mild and limited to these areas of the skin.
In some cases, the reaction of the skin to radiation may be more pronounced and occupy a larger area of \u200b\u200bthe breast. This mainly happens when:
- You have fair skin and are very susceptible to sunburn.
- You have a large breast.
- Your radiation therapy is performed after your mastectomy and requires a higher dose of radiation.
- You have recently received chemotherapy.
Here are some ways to reduce the appearance of skin reactions to radiation:
- Wear loose, loose-fitting clothing, preferably cotton.
- If the skin around the breast is especially sensitive and irritable, try wearing a loose cotton bra.
- You don't need to wear a bra at all.
Usually, such changes on the part of the skin occur gradually and with a weekly examination by a doctor, they can be prevented. Fortunately, skin irritation from radiation is temporary. Your doctor may give you certain ointments, medications to help soften your skin reactions.
Skin reactions after completion of radiation therapy
After the course of radiation therapy is completed, the negative effects of the skin can still be observed for one to two weeks, after which they gradually begin to disappear. Redness and irritation will gradually disappear from the next week. The natural skin color will return a little longer. Moreover, for six months or longer, you may notice that the irradiated areas of the skin are somewhat darker or, on the contrary, more pink than usual.
In some patients, the dark tint of the irradiated skin can be observed even for more than a year after treatment. In some cases, thin blood vessels may appear on the irradiated skin areas. These are the so-called telangiectasias. These vessels are by no means signs of cancer recurrence. Unfortunately, they do not go away on their own and you may need the help of a vascular surgeon.
If you smoke, quitting smoking can sometimes improve your situation. Hyperbaric oxygenation - treatment with pure oxygen under high pressure - can sometimes help. For the treatment of such telangiectasias, laser radiation is now widely used.
Here are some tips for those undergoing radiation therapy:
- During treatment, it is recommended to avoid exposure to sunlight on the irradiated area,
- Wear high collar clothing.
- Always wear clothes.
- It is recommended to wear loose clothing, even a size larger - it creates coolness for the skin and does not irritate the irradiated areas.
- If you take a bath, shower or swim in the pool, you should lubricate the irradiated skin with petroleum jelly to avoid irritation with chlorinated water.
Sensitive skin areas
The skin of the inner upper corner of the mammary gland is most susceptible to the irritant effects of radiation for several reasons. The angle of the radiation beam is parallel to the skin in this place and therefore passes a larger area of \u200b\u200btissue, this area of \u200b\u200bthe breast is more exposed to radiation.
In addition, when in the armpit it also turns out to be more irritated, since in addition to the effects of radiation, there is friction of the skin in this place, and its irritation by sweat and hair.
Another area that is more irritated than other areas is the fold under the breast, as this area is irritated by the bra, and the radiation beam in this area also runs parallel to the skin and there is friction.
Skin Care Tips During Radiation Therapy Here are some tips for skin care during radiation therapy to reduce irritation and help it recover more quickly after treatment is complete:
- Use warm water when showering or bathing; try to avoid hot water as it irritates your skin.
- During the shower, the water should not pour directly onto the mammary gland.
- Avoid soaps with harsh scent; instead, it is recommended to use soaps with moisturizing ingredients (like Dove).
- In order to avoid skin redness and irritation, make sure that there is no friction between different parts of the skin (we mentioned above about these areas where friction usually occurs).
In order to avoid rubbing your skin, try to avoid hand-to-body contact whenever possible. Try to wear loose clothing that does not fit snugly around your body. It is recommended that you wear a bra that will tighten the dangling chest, thereby avoiding friction in the folds. If you have large breasts and cannot wear a bra, place a soft cotton or flannel cloth under the breast crease to avoid chafing and irritation.
Remember that there is always an infection in the folds of the skin - the yeast Candida. In such folds (for example, under the mammary gland), where there is appropriate moisture and heat, they develop well. A symptom of such a yeast infection is skin redness, itching, and some pale skin discharge. If you have such an infection, take care of it before starting treatment. antifungal ointments are usually used. To choose one or another remedy, you must consult with a dermatologist.
Regularly use a starch (but not talcum) based powder on the rubbing area of \u200b\u200byour skin. The powder absorbs excess moisture and gives the skin a pleasant fresh scent. Powder should be applied with a soft brush or powder directly from the bottle. Make sure that the powder is evenly distributed. If your doctor prescribes any ointments or creams, first apply them, and then dust with powder.
This primarily applies to facial skin tumors. Considering that there are basal cell cancers on the skin of the face, radiation therapy provides a high percentage of cures with good cosmetic effect.
Radiation therapy for skin cancer has the following advantages over surgical treatment: it is a bloodless, painless method of treatment, and has an excellent cosmetic effect.
Indications for radiation therapy for skin cancer
1) with primary skin cancers;
2) with metastatic skin cancers;
3) with a prophylactic purpose after surgery;
4) with relapses.
Radiation therapy for skin cancer
Fractionated irradiation method. Its essence is. that within 10-12 days, treatment is carried out in relatively fractional doses, and the total dose is brought to 4000 glad.
The fractional irradiation method has the advantage that tumor tissues are damaged more, and healthy tissues are spared more than with the old methods; on the other hand, the reactivity of the tissues surrounding the tumor remains, which largely determines the therapeutic effect.
The positive features of the fractionated method of irradiation include the influence of the time factor. Prolongation of treatment up to 12-15 days ensures the effect of X-rays on all cancer cells, since during this period all cells undergo the mitosis phase and, therefore, are exposed to radiation.
In the literature that we have collected on the treatment of skin cancer, the idea is that all efforts should be directed towards achieving a cure after one course of X-ray therapy.
The currently accepted principle of treating malignant neoplasms is to give a maximum dose during one course, compatible with the need to sparing healthy tissues. Repeated irradiation due to the cumulative effect of X-rays is dangerous - they entail a change in vascularization, damage to the surrounding healthy tissue, and cause necrotic changes.
Based on this, fractionated irradiation with a high total dose is recognized as the most effective method that guarantees the elimination of the cancer focus in one course of treatment.
Concentrated short-focus method of irradiation according to Schaul. The short-focus irradiation method is based on the principle of creating conditions for the distribution of X-ray energy, similar to those that exist when using radium, despite the fact that the wavelength of these two types of radiation is not the same. From the point of view of modern X-ray biology, the therapeutic and biological effect depends only on the amount of absorbed energy, be it the energy of y-rays or the energy of X-rays. The qualitative aspect of the radiation is not given significant importance.
Based on the equivalence of y- and x-rays, Shaul believes that the greater effectiveness of radium therapy is due only to a more appropriate distribution of 7-rays. It is appropriate to note here that the issue of the spatial distribution of the dose during radiation therapy is extremely relevant, especially in the treatment of malignant neoplasms. The relationship between the energy absorbed by the tumor and the adjacent tissues becomes extremely important.
A difficulty with radiation therapy for skin cancer is that the sensitivity differences between tumor cells and cells of the surrounding tissue are often insufficient. That is why the currently accepted principle of using radiation therapy for malignant neoplasms is based on the desire not only to destroy the tumor as much as possible, but also to spare the surrounding tissues as much as possible.
When radium is brought directly to the affected focus, the greatest effect of the rays on the site of application of radium and the minimum effect on the surrounding tissues is achieved, since the intensity of the effect of radiation on the depth and to the periphery sharply decreases.
In this respect, the method of concentrated close-focus irradiation is aimed at creating the same conditions.
According to Schaul, the method he proposed should be an imitation of radium therapy; and indeed it began to be successfully used instead of radium therapy in some localizations of skin cancer, oral cavity, as well as in malignant melanomas, etc. Treatment is carried out using a special X-ray tube, in which the anode in the form of a hollow cylinder is brought out.
Radiation therapy for skin cancer by this method is carried out at a single dose of 400 - 800 glad, and the total dose is 6000 - 8000 glad.
Results of radiation therapy for skin cancer
Results depend on:
1) morphological picture;
2) localization and soil on which cancer develops;
3) methods of treatment.
Basal cell carcinoma is most successfully treated with X-ray therapy. The mixed form is more resistant than the purely basocellular form. Squamous cell carcinoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer. The success of treatment with this form depends on the timeliness of the diagnosis.
In some locations (corner of the eye, pinna), the effectiveness of radiation therapy for skin cancer decreases.
The prognosis sharply worsens in case of damage to bone and cartilage tissue. This is explained by the fact that bone and cartilage tissues, due to their anatomical and physiological properties, cannot respond to X-ray irradiation with an appropriate reaction.
The soil on which the neoplasm has developed is also important. The reason for the worst treatment results for cancer caused by lupus and scars is that the surrounding tissue, being weakened under the influence of the underlying disease, is not able to respond with the desired response to X-rays.
The reason for the failure of radiation therapy for skin cancer is that sometimes the proliferation of epithelial tissue in the deeper parts of the tumor stops for a very short time, and then starts again. This can be the result of inadequate selection of beam quality, inadequate filtration and dose. To select a carcinocidal dose in relation to deeply located cells, it is necessary to use filtered beams, appropriate voltage and cross-radiation. It should be used as large as possible, without damaging normal tissue.
Failures are rare due to the presence of resistant cells, especially in basocellular epitheliomas. It should also be remembered that not all cells that make up a malignant neoplasm have the same degree of sensitivity; some of the cells in the same tumor may be very resistant.
Patients after radiation therapy for skin cancer should be monitored every six months for 5 years. Failure to comply with this rule is often the cause of serious consequences.
At stages 1 and 2, radiation therapy for skin cancer is performed under the conditions of short-focus X-ray therapy. A single dose is 300 - 400 glad, total - 5000 - 7000 glad. Doses of 500 - 600 rad per session significantly reduce the treatment time, but leave great changes on the skin, which gives worse cosmetic results. Cure at stage 1 is observed in 95-98%, and at stage 2 - in 85-87% of cases.
At stage 3, radiation therapy should be carried out under the conditions of deep X-ray therapy, on a cesium unit, and in some cases - on a telegamma unit. A single dose should not exceed 250 rad. The question of the total dose is decided in each individual case, depending on the size of the lesion. If only one radiation therapy raises doubts about the possibility of achieving good results, then after attenuation of the radiation response, surgical or electrosurgical methods of treatment can be recommended. At stage 4, treatment (if one can be carried out) must begin with radiation (deep X-ray therapy or telegammotherapy).
After radiation therapy, in some cases, it is possible to perform excision of the tumor with or without plastic surgery, depending on the condition and localization of the pathological process. In case of X-ray cancer, which developed on the basis of scars, and recurrence of skin cancer after radiation treatment, surgical treatment is indicated. The volume should not be embarrassing, since tumor growth does not spare the patient and leads to severe disability.
The article was prepared and edited by: surgeonIn oncology, it is a method of treating tumor diseases using ionizing radiation. Its consequences are much less than the benefits it brings in the fight against a tumor. This type of therapy is used in the treatment of half of cancer patients.
Radiation therapy (radiation therapy) is a treatment that uses a stream of ionized radiation. These can be gamma rays, beta rays, or X-rays. Such types of rays are able to actively influence on, leading to disruption of their structure, mutation and, ultimately, to death. Although exposure to ionized radiation is harmful to healthy cells in the body, they are less susceptible to radiation, allowing them to survive despite exposure. In oncology, radiation therapy negatively affects the expansion of tumor processes and slows down the growth of malignant tumors. Oncology after radiation therapy becomes less of a problem, since in many cases the patient's condition is improving.
In addition to surgery and chemotherapy, radiation therapy makes it possible to achieve complete recovery of patients. Although radiation therapy is sometimes used as the only therapy, it is more often used in combination with other cancer-fighting methods. Radiation therapy in oncology (reviews of patients are generally positive) has become a separate medical field these days.
Types of radiation therapy

Remote therapy is a type of treatment in which the radiation source is located outside the patient's body, at a certain distance. Remote therapy can be preceded by the ability to plan and simulate the operation in three-dimensional form, which allows more precise exposure of the tissues affected by the beams.
Brachytherapy is a method of radiation therapy in which the radiation source is located in the immediate vicinity of the tumor or in its tissues. Among the advantages of this technique is the reduction of the negative effects of radiation on healthy tissues. In addition, with a point effect, it is possible to increase the radiation dose.
To achieve the best results, the required radiation dose is calculated and planned in preparation for the radiation therapy.
Side effects

Radiation therapy in oncology, the consequences of which a person feels on himself for a long time, can still save a life.
Each person's response to radiation therapy is individual. Therefore, all the side effects that may occur are very difficult to predict. Let's list the most common symptoms:
- Decreased appetite. Most of the patients complain of poor appetite. In this case, it is necessary to eat food in small quantities, but often. Nutrition in case of a lack of appetite can be discussed with your doctor. The body undergoing radiation therapy needs energy and nutrients.
- Nausea. One of the main causes of decreased appetite is nausea. Most often, this symptom can be found in patients who are undergoing radiation therapy in the abdominal area. In this case, vomiting may also appear. The doctor must be immediately informed of the situation. The patient may need to prescribe antiemetics.
- often occurs as a result of radiation therapy. If diarrhea occurs, you should drink as much fluid as possible to prevent dehydration. This symptom should also be reported to your doctor.
- Weakness. During the course of radiation therapy, patients significantly reduce their activity, experiencing apathy and being in poor health. Almost all patients who have undergone a course of radiation therapy face this situation. It is especially difficult for patients to visit the hospital, which periodically need to be made. For this period of time, you should not plan things that take away physical and moral strength, you should leave the maximum time for rest.
- Skin problems. 1-2 weeks after the start of radiation therapy, the skin in the zone of exposure to radiation begins to redden and peel off. Sometimes patients complain of itching and pain. In this case, you should use ointments (on the recommendation of a radiologist), aerosol "Panthenol", creams and lotions for the care of baby skin, refuse cosmetics. Rubbing irritated skin is strictly prohibited. The area of \u200b\u200bthe body where skin irritation has occurred should be washed only with cool water, temporarily refusing to take baths. It is necessary to rid the skin of direct sunlight and wear clothes using natural fabrics. These actions will help relieve skin irritation and relieve pain.
Reducing side effects

After completing a course of radiation therapy, your doctor will advise you on how to behave at home, taking into account your particular case, to minimize side effects.
Anyone who knows what radiation therapy is in oncology has a good idea of \u200b\u200bthe consequences of this treatment. Those patients who are being treated with radiation therapy for neoplastic disease must adhere to the doctor's recommendations, promoting successful treatment and trying to improve their well-being.
- Spend more time resting and sleeping. The treatment requires a lot of extra energy and you can tire quickly. The state of general weakness sometimes lasts another 4-6 weeks after the treatment has already ended.
- Eat well while trying to prevent weight loss.
- Do not wear tight clothing with tight collars or belts in the exposed areas. It is better to prefer old suits in which you feel comfortable.
- Be sure to inform your doctor about all medications you are taking so that he can take this into account when treating.
Radiation therapy

The main direction of radiation therapy is to maximize the effect on tumor formation, while minimally affecting other tissues. To achieve this, the doctor needs to determine exactly where the tumor process is, so that the direction and depth of the beam will allow them to achieve their goals. This area is called the radiation field. When remote irradiation is performed, a mark is applied to the skin to indicate the area of \u200b\u200bthe radiation exposure. All adjacent areas and other parts of the body are protected by lead screens. The session, during which the radiation is performed, lasts several minutes, and the number of such sessions is determined by the radiation dose, which, in turn, depends on the nature of the tumor and the type of tumor cells. During the session, the patient does not experience discomfort. During the procedure, the patient is alone in the room. The doctor controls the course of the procedure through a special window or with a video camera in the next room.
In accordance with the type of neoplasm, radiation therapy is either used as an independent method of treatment, or is part of a complex therapy together with surgery or chemotherapy. Radiation therapy is applied topically to irradiate specific areas of the body. Often, it contributes to a noticeable reduction in the size of the tumor or leads to a complete cure.
Duration

The time for which the course of radiation therapy is designed is determined by the specifics of the disease, doses and the method of radiation used. Gamma therapy often lasts 6-8 weeks. During this time, the patient manages to take 30-40 procedures. Most often, radiation therapy does not require hospitalization and is well tolerated. Some indications require radiation therapy in a hospital setting.
The duration of the course of treatment and the dose of radiation are directly dependent on the type of disease and the degree of neglect of the process. The duration of treatment with intracavitary irradiation lasts much less. It can consist of fewer treatments and rarely lasts more than four days.
Indications for use
Radiation therapy in oncology is used to treat tumors of any etiology.
Among them:
- brain cancer;
- breast cancer;
- cervical cancer;
- laryngeal cancer;
- pancreas cancer;
- prostate cancer;
- spine cancer;
- skin cancer;
- sarcoma of soft tissues;
- stomach cancer.
Radiation is used to treat lymphoma and leukemia.
Sometimes, radiation therapy can be given prophylactically without evidence of cancer. This procedure serves to prevent the development of cancer.
Radiation dose
The volume of ionizing radiation absorbed by the tissues of the body is called. Previously, the unit of measurement of radiation dose was the rad. Gray is now serving this purpose. 1 Gray equals 100 rad.
Different tissues tend to withstand different doses of radiation. So, the liver is able to withstand almost twice as much radiation as the kidneys. Breaking the total dose into pieces and irradiating the affected organ day after day will increase damage to cancer cells and reduce healthy tissue.
Treatment planning

The modern oncologist knows everything about radiation therapy in oncology.
There are many types of radiation and methods of radiation in the arsenal of a doctor. Therefore, a properly planned treatment is the key to recovery.
With external beam radiation therapy, the oncologist uses a simulation to locate the area to be treated. During the simulation, the patient is placed on the table, and the doctor determines one or more radiation ports. During the simulation, it is also possible to perform computed tomography or other diagnostic method in order to determine the direction of radiation.
Irradiation zones are marked with special markers indicating the direction of radiation.
In accordance with the type of radiation therapy chosen, the patient is offered special corsets that help fix different parts of the body, eliminating their movement during the procedure. Sometimes special protective shields are used to help protect adjacent tissues.
Based on the result of the simulation, the radiation therapy specialists will decide on the required radiation dose, delivery method and number of sessions.
Diet
Nutritional advice can help you avoid or reduce side effects from treatment. This is especially important for radiation therapy in the pelvic and abdominal regions. Radiation therapy and have a number of features.
You need to drink plenty of fluids, up to 12 glasses a day. If the liquid has a high sugar content, it must be diluted with water.
Food intake is fractional, 5-6 times a day in small doses. Food should be easy to digest: food containing coarse fiber, lactose and fat should be excluded. It is advisable to follow such a diet for another 2 weeks after the therapy. Then you can gradually introduce foods with fibers: rice, bananas, apple juice, mashed potatoes.
Rehabilitation
The use of radiation therapy affects both tumor and healthy cells. It is especially harmful for cells that divide rapidly (mucous membranes, skin, bone marrow). Radiation generates free radicals in the body that can harm the body.
Work is underway to find a way to make radiation therapy more targeted so that it only targets tumor cells. A gamma knife device appeared, which is used to treat tumors of the neck and head. It provides a very precise effect on small tumors.
Despite this, almost everyone who has received radiation therapy suffers from radiation sickness to varying degrees. Pain, swelling, nausea, vomiting, hair loss, anemia - these symptoms are ultimately caused by radiation therapy in oncology. Treatment and rehabilitation of patients after radiation sessions are a big problem.
For rehabilitation, the patient needs rest, sleep, fresh air, good nutrition, the use of immune system stimulants, detoxification agents.
In addition to a health disorder that is caused by a serious illness and its harsh treatment, patients experience depression. Rehabilitation activities often require sessions with a psychologist. All these activities will help to overcome the difficulties that radiation therapy has caused in oncology. Reviews of patients who underwent a course of procedures indicate the undoubted benefits of the technique, despite the side effects.